Private Adoption: What Are the Common Legal Issues
Private adoption is a deeply rewarding process that allows hopeful parents to expand their families and provide children with loving homes.
However, it is also a complex legal journey that requires careful navigation.
Prospective adoptive parents and birth parents must understand the legal issues that can arise to ensure a smooth and ethical adoption process.
Below, we explore some of the most common legal challenges in private adoptions when it comes to:
- Working with Birth Parents
- Interstate Adoption Regulations
- Termination of Parental Rights
- Required Consent
But let’s first get a better understanding of the private adoption process.
What Is Private Adoption
Private adoption, also known as independent adoption or domestic adoption, is a process where prospective adoptive parents work directly with a private adoption attorney or agency to adopt a child, typically an infant, from within the United States.
In this type of adoption, birth parents voluntarily choose to place their child for adoption and have the opportunity to select the adoptive family.
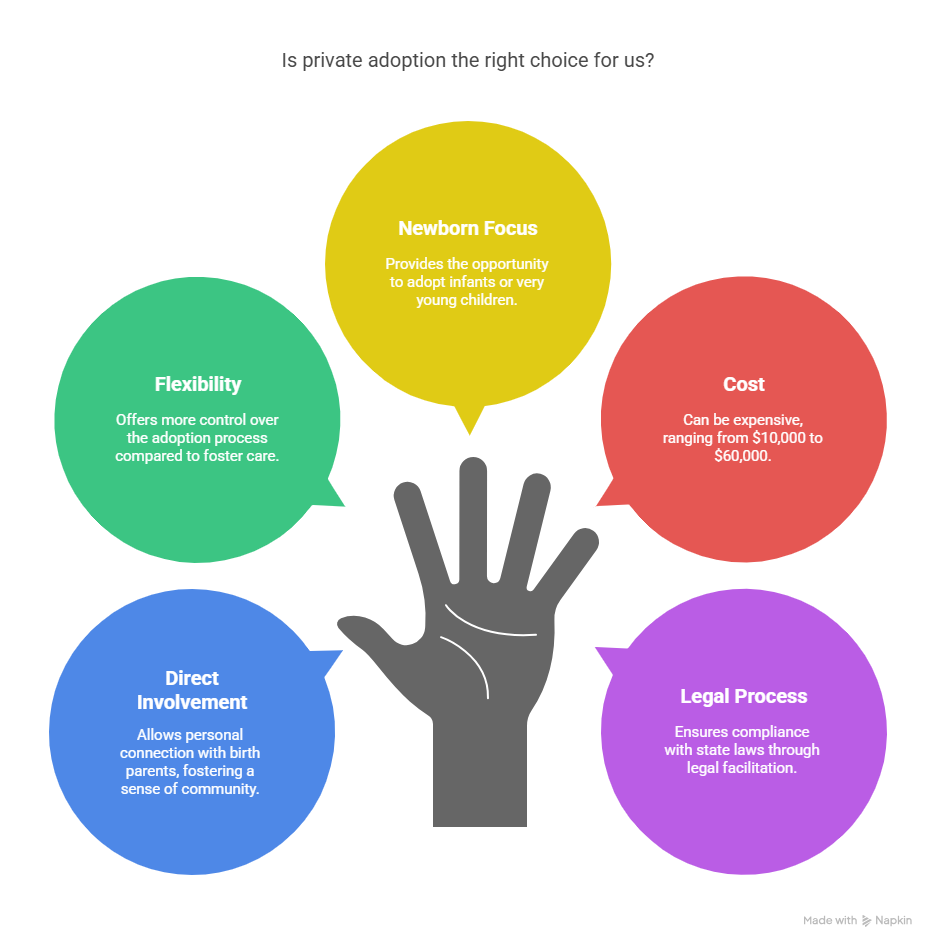
Key aspects of private adoption include:
- Direct involvement: Birth parents and adoptive parents can learn about each other before agreeing to the adoption.
- Flexibility: Private adoptions generally offer more flexibility compared to adoptions through the foster care system.
- Newborn focus: This method often involves the adoption of infants or very young children.
- Cost: Private adoptions can be more expensive than foster care adoptions, with costs ranging from $10,000 to $60,000.
- Legal process: The adoption is facilitated by an adoption attorney or agency to ensure compliance with state laws.
- Home study: Prospective adoptive parents must complete a home study as part of the approval process.
- Openness: Private adoptions often involve some degree of openness between birth and adoptive families.
While private adoption offers many benefits, such as more control over the process and potentially faster placements, it’s important to note that it can be more costly than foster care adoptions through the foster care adoption system.
Prospective adoptive parents should carefully consider their options and consult with adoption professionals to determine the best path for their family.
What Are the Main Benefits of Private Adoption
The main benefits of private adoption include:
- Faster Process: Private vs foster care adoptions adoption is generally quicker than foster care adoption, as it avoids long waiting lists and bureaucratic delays. Families can often bring the child home within a year.
- More Control and Flexibility: Adoptive parents have greater control over the process, including selecting the birth mother and child they wish to adopt. This also allows for a more personalized match between families.
- Direct Communication: Birth parents and adoptive families often have the opportunity to meet and build a relationship, which can make the process more transparent and reassuring for both parties.
- Focus on Infants: Private adoption typically involves newborns or very young children, allowing adoptive parents to experience milestones such as first steps and early development.
- Access to Medical and Genetic History: Adoptive families can learn about the child’s medical and genetic background directly from the birth parents, reducing potential surprises in the future.
- Support for Birth Parents: Whether through an adoption attorney or an adoption agency, birth mothers are offered and provided counseling, financial assistance, and help with medical care for birth mothers, ensuring they receive adequate support during the process.
These advantages make private adoption an appealing option for families seeking a more tailored adoption experience, though it is important to consider costs and legal complexities associated with this route.
Private vs Foster Care Adoptions Adoption: What’s the Difference
Private adoption and foster care adoptions differ in several key areas, including cost, process, timeline, and the characteristics of children available for adoption.
Below is a comparison:
| Aspect | Private Adoption | Foster Care Adoptions |
|
Cost |
Significantly higher, ranging from $20,000 to $50,000 due to legal, medical, and professional fees. | Much lower, often under $3,000, with subsidies often provided by the state. |
|
Children Available |
Typically infants or newborns placed voluntarily by birth parents. | Primarily older children or sibling groups removed from unsafe situations. |
|
Wait Times |
Shorter on average, depending on preferences and match availability. | Longer due to efforts to reunify children with biological families (can take months to years). |
|
Biological Parent Involvement |
Allows for adopting parents to have more control over the amount of contact up until the adoption is finalized. Post-adoption contact is left to the discretion of the parties and the best interest of the child. | Limited or no contact; varies based on case specifics and agreements. |
|
Process |
Managed by private agencies or attorneys; adoptive parents often have more control over selecting the child and birth parents. | Facilitated by foster care agencies; involves more oversight and less direct control for adoptive parents. |
|
Emotional Needs of Children |
Usually fewer emotional or behavioral challenges due to early placement as infants. | Children may have experienced trauma or neglect and may require additional support. |
In summary, private adoption offers more control, quicker placement of newborns, and opportunities for openness but comes at a higher cost. Foster care adoptions is more affordable and provides homes for children in need but often involves older children with unique emotional needs and longer timelines.
***
Now that we have a better understanding of the private adoption process, let’s look at some of the legal ramifications that will need to be navigated.
Working with Birth Parents
One of the most significant legal issues in private adoptions involves the rights and roles of birth parents.
Clear communication and legal agreements are essential to ensure that both the adoptive and birth parents understand their responsibilities and expectations.
Some potential challenges include:
- Revocation of Consent: In some cases, birth parents may change their minds after initially consenting to the adoption, leading to potential legal disputes.
- Open vs. Closed Adoptions: Determining the level of post-adoption contact between the child and birth parents can be a legal issue if expectations are not properly documented.
The primary difference between open and closed adoption lies in the level of contact and information shared between the biological parents, adoptive parents, and the adopted child.
Open Adoption
- Definition: In an open adoption, there is ongoing communication and sharing of information between the biological and adoptive families. This can include direct contact, such as visits, phone calls, or emails, or mediated communication through a third party.
- Types:
- Fully Open Adoption: Direct and active contact among birth parents, adoptive parents, and the child.
- Semi-Open Adoption: Communication is mediated through a third party (e.g., caseworker or attorney) to maintain some level of privacy.
- Pros:
- Helps the child maintain a sense of identity and connection to their biological family.
- Provides access to updated medical history for the child.
- Allows birth parents to remain involved in the child’s life, which can ease feelings of grief.
- Facilitates a positive relationship between all parties.
- Cons:
- Potential for boundary issues if expectations are not clearly defined.
- It may be emotionally challenging for some families to navigate.
- Types:
Closed Adoption
- Definition: In a closed adoption, there is no contact or exchange of identifying information between the biological and adoptive families. The adoption records are sealed, and the child typically has no access to their birth parents’ identity until adulthood (if allowed by law).
- Pros:
- Provides privacy and emotional closure for both birth and adoptive families.
- Offers a “clean slate” for adoptive families to start their life with the child.
- Cons:
- The child may struggle with unanswered questions about their identity or family history.
- Limited access to updated medical information.
- Can create feelings of abandonment or loss in the child.
Birth Father’s Rights: If the birth father is unknown or contests the adoption, legal complications may arise, potentially delaying or preventing the adoption.
Interstate Adoption Regulations
Many private adoptions involve adoptive parents and birth parents residing in different states. In these cases, the Interstate Compact on the Placement of Children (ICPC) governs the legal requirements for transferring the child across state lines. Key considerations include:
- State-Specific Adoption Laws: Adoption laws vary widely from state to state, and what is permissible in one state may not be legal in another.
- ICPC Approval: Before the child can be taken to the adoptive parents’ home state, both states involved must approve the adoption plan, which can cause delays if not properly managed.
- Legal Representation: Having an attorney who understands interstate adoption laws is crucial to avoiding unexpected legal hurdles.
Terminating Parental Rights
Before an adoption can be finalized, the legal rights of the biological parents must be terminated. Terminating parental rights in California is one of the most critical legal steps in the process.
Challenges may include:
- Voluntary vs. Involuntary Termination: In most cases, parental rights are voluntarily relinquished, but if a parent is unwilling, the court may need to determine if involuntary termination is justified.
- Court Proceedings: If a court needs to terminate parental rights, there must be evidence of abandonment, neglect, or unfitness, which can be a lengthy legal process.
- Appeals and Contests: In some instances, birth parents or relatives may challenge the termination, leading to delays or legal battles.
Required Consent
Consent is a fundamental legal requirement in private adoptions. Adoption without parental consent may not be legally valid. Important consent-related legal issues include:
- Timing of Consent: Some states allow birth parents to sign consent documents immediately after birth, while others require a waiting period.
- Revocation Periods: Many states provide a period in which birth parents can revoke their consent, creating potential emotional and legal challenges for adoptive parents.
- Proper Execution: Consent must be given voluntarily and in accordance with state laws, typically before a judge or a licensed agency representative.
***
Navigating the legal landscape of private adoption requires careful planning and legal expertise.
Working with an experienced adoption attorney can help prospective parents and birth families address common legal challenges, ensuring a smooth and ethical adoption process.
By understanding the complexities of birth parent rights, interstate regulations, parental rights termination, and consent requirements, all parties involved can move forward with confidence and clarity.
If you are considering private or foster care adoptions and want greater clarification on the processes, please contact the Adoption Law Firm. We can provide an initial consultation to help you understand the options available to you and get you on your way to creating a lifetime bond.
***
The information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. This content is not intended to create an attorney-client relationship. The information presented should not be construed as legal counsel or a substitute for seeking professional legal advice. Any opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Adoption Law Firm. Readers should not act or refrain from acting based on the information provided without first consulting a licensed attorney for advice specific to their individual situation.
About the Adoption Law Firm
Your dream of building a family through adoption is sacred – and we’re here to help make it real. At the Adoption Law Firm, we have been guiding parents and children toward each other with heartfelt dedication for over 30 years.
We specialize in all aspects of California adoption laws, specializing in:
- Adult adoption
- Child adoption
- Foster care adoption
- Guardianship to adoption
- Legal guardianship
- Birth mother representation
We understand that adoption is a life-changing journey filled with hope, anticipation, and profound meaning. That’s why we stand beside you with both legal expertise and genuine care every step of the way.